|
Lancashire Churches
Step into Invitation To Prayer, a haven where you can immerse yourself in the beauty and strength of prayers.
Updated 26 January 2003 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
An enthusiast's look at the architecture and history of the churches of the Red Rose County |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Rental Property Tax Deductions Every Landlord Should KnowIf you own rental property, understanding tax deductions is essential for protecting your profits each year. Many landlords miss out on valuable opportunities to lower their tax bills simply because they’re not aware of what’s deductible. From mortgage interest to maintenance costs, every eligible expense makes a difference. Getting the details right could save you a significant amount when it’s time to file. Want to make sure you’re not overpaying? There’s more you need to know. Defining Rental Income and Its Tax ImplicationsUnderstanding rental income is crucial for landlords when preparing their tax returns. Rental income encompasses the total amount received from tenants, which includes regular rent payments, advance rent, and any fees paid by tenants. According to IRS regulations, this income must be reported on Form 1040, Schedule E. It is also important to note that security deposits must be accounted for if they are retained as final payment for any damages or unpaid rent. Additionally, any services rendered in lieu of cash payments should be assessed at their fair market value and included as part of rental income. It is vital for landlords to maintain accurate records of all rental transactions and activities. This includes documenting any expenses that tenants may incur on behalf of the landlord, as well as any refunds that may be processed. Such financial records are essential for ensuring compliance with tax obligations and providing a clear picture of the rental income's overall financial impact. Common Deductible Expenses for Rental PropertiesOwning and managing rental properties presents a range of expenses that can be deducted from taxable income. Landlords may deduct mortgage interest, property taxes, and necessary repairs, which are considered standard operational costs essential for maintaining the property. Additionally, expenses related to travel—such as mileage and fuel—are also deductible, alongside payments made for business-related services, including those for maintenance workers. Advertising costs incurred to attract tenants are also eligible for deduction. It is important to note that when a tenant pays advance rent or a security deposit that will be applied as a final payment, the landlord must report this amount as rental income in the year it is received. Furthermore, landlords can benefit from depreciation, which allows the recovery of the market value of the property over time. However, deductions related to depreciation must adhere to passive activity loss rules, which can limit the extent to which losses may offset other income. This framework provides landlords with a structured approach to managing their taxable income through legitimate expense deductions. Non-Deductible Rental Property ExpensesWhen managing a rental property, it is essential to understand which expenses qualify as tax-deductible. Certain costs are expressly excluded from deductions. Personal expenses, including travel for non-business reasons and household utilities, cannot be claimed as rental expenses on tax forms or Schedule E. Additionally, payments for local benefit taxes, such as those for sidewalks or road improvements, are non-deductible since they enhance the property's fair market value. Moreover, there are specific rules that govern the deductibility of security deposits. If a security deposit is intended to be refunded, it cannot be deducted. Partial ownership of a property may also impose limitations on the deductibility of expenses you can claim. Further complicating matters, expenses incurred for real estate that is not placed in service or is actively listed for sale are not eligible for tax deductions. It is crucial for property owners to be aware of these restrictions to ensure compliance with tax regulations and to accurately assess their taxable income. Understanding these parameters can aid in better financial planning and reporting. Procedures for Reporting Rental Income and ExpensesReporting rental income and expenses on your federal tax return necessitates precise and accurate documentation. As a landlord, it is imperative to report all rental income, including advance rent and amounts withheld from security deposits due to tenant breaches of the rental agreement. To manage this process effectively, landlords should utilize IRS Schedule E Forms for each property. This will allow for a detailed breakdown of income, refunds, and various expenses such as repairs, maintenance, mortgage interest, and legal fees. Landlords must also be aware of passive activity loss rules, which may limit the deductibility of losses. It is essential to document the fair market value of services rendered or other considerations received in the course of rental operations. Adhering to these guidelines helps ensure compliance with federal tax regulations. Proper reporting and record-keeping not only facilitate accurate tax filings but also mitigate potential issues with tax authorities. Recordkeeping Practices for LandlordsEffective recordkeeping is essential for efficient rental property management and ensuring compliance with tax regulations. Landlords should maintain comprehensive records for each property, which includes documenting rental income, payment methods (such as checks and direct deposits), expenses incurred, security deposit amounts received, and mileage rates related to repairs and maintenance. To facilitate this process, the use of rental property accounting software or detailed spreadsheets is advisable. Such tools enable landlords to accurately track various financial activities, including security deposits, advance rent payments from tenants, and any amendments to rental agreements. It is important to retain these records in an organized manner, making them easily accessible for a minimum of three years following the submission of tax returns. This practice not only aids landlords in identifying available deductions but also ensures compliance with loss rules pertaining to passive activities. Furthermore, being organized enhances preparedness for potential audits, refunds, amended returns, or adherence to state and local regulations. In summary, diligent recordkeeping is a fundamental aspect of managing rental properties and fulfills important legal and financial obligations. Key IRS Forms and Resources for Rental Property OwnersManaging rental properties requires familiarity with specific IRS forms to ensure accurate reporting of income and proper claiming of deductions. As a landlord, it is essential to utilize Schedule E (Form 1040) to report rental income, advance rent, and any payments made, as well as to list deductible expenses related to the property. Additionally, Form 4562 is relevant for landlords looking to recover property costs through depreciation, which can reduce taxable income over time. In instances where rental activities are classified as a business, it may be necessary to file Schedule C to report income and expenses more comprehensively. For any payments exceeding $600 made to third-party contractors, Form 1099-MISC must be included in filings to ensure compliance with IRS reporting requirements. Furthermore, landlords would benefit from consulting IRS Publication 527, which provides detailed instructions on various aspects of rental tax regulations. These include guidelines on passive activity loss rules, handling security deposits, and understanding the differences between repairs and maintenance as well as the deductions available. Accurate tax filings are vital for avoiding potential issues with tax fraud, underscoring the importance of adhering to these forms and resources when managing rental properties. ConclusionUnderstanding rental property tax deductions helps you keep more of your rental income. By accurately documenting expenses and knowing which costs you can deduct, you’ll minimize your tax burden and stay compliant with IRS rules. Don’t overlook the importance of good recordkeeping and using the right tax forms. If your situation feels complicated, it’s wise to consult a tax professional. With the right approach, you can maximize your deductions and protect your investment. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
East window, Aldingham, St Cuthbert Stained glass of 1964 designed by Harcourt Doyle showing Christ, local workers, and wildlife. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Aughton, St Michael Its Decorated tower has characteristics that can be seen at nearby Halsall and Ormskirk. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dolphinholme, St Mark "One would have to search far and search long in England to find village churches to vie with ... Dolphinholme of 1897 ...": Pevsner. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
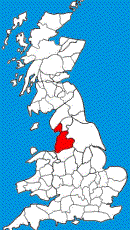
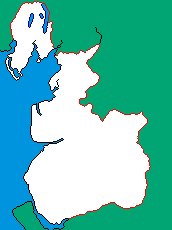
The maps show the location of Lancashire and the extent of the historic county.
Lancashire stretches from the Coniston and Windermere areas of the Lake District, down to the Furness peninsula and Walney Island, across the sands of Morecambe Bay to the Lune valley, through Bowland, the Fylde, the western Pennines, and south to the areas around Southport, Liverpool, Manchester and Warrington. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Thurnham, St Thomas & St Elizabeth The Gillow Mausoleum. A Victorian tomb in the Egyptian style for a family who were renowned Lancaster furniture makers. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Photographs and text © Tony Boughen |
|||||||||||||||||||||